Vietnam GDP growth to reach 8.1% in 2021: Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs expected exports to be Vietnam’s major driving force for economic recovery.
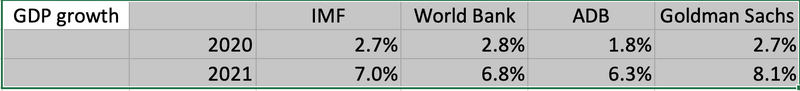
In 2020, Vietnam’s GDP growth is set to slow to 2.7% and rebound to 8.1% next year, according to the US-based investment bank Goldman Sachs.
| Forecast for Vietnam's GDP growth. |
Goldman Sachs’ 2.7%-GDP growth forecast for Vietnam in its first ever macro-economic report on the country, one of the fastest growing economies in Asia, is lower than that of the World Bank (2.8%), but higher than ADB’s 1.8%.
While Vietnam’s economy growth slowed to 3.8% and 0.4% in the respective first and second quarters, the US bank expected GDP growth to quickly recover in the third quarter, mainly thanks to public investment, retail’s revenue and exports.
Notably, Goldman Sachs expects exports to be Vietnam’s major driving force for economic recovery. In the first eight months of 2020, Vietnam’s trade surplus reached an all-time high of US$13.5 billion, representing a 150% increase compared to the same period of last year (US$5.47 billion)
The bank’s report pointed to three major advantages contributing to a growing export turnover.
Firstly, Vietnam holds significant advantage in regional supply chains as the country is located in close proximity with China.
The labor cost in Vietnam is also considered competitive, which remains at half of China’s. For example, the minimum wage in major cities such as Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City is regulated at US$190 per month, significantly lower than the US$360 in Shanghai. Meanwhile, the minimum wage in other cities in Vietnam and China were estimated at US$132 and US$220 per month, respectively.
According to Goldman Sachs, these factors led to a shift in production of firms in the fields of textile and footwear from China to Vietnam, especially during the US – China trade war. Since 2010, the FDI investment capital that was initially bound to China, South Korea, Japan or countries in ASEAN have now flowed to Vietnam.
Meanwhile, the fact that Vietnam is currently member of a number of free trade agreements (FTAs) with major trading partners could shield the country from growing protectionism globally. For instance in 2019, at the peak of the US – China trade tension, Vietnam’s exports had not been much impacted, which eventually led to a record trade surplus of US$11.12 billion that year.
In the future with the presence of the EU – Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA), Goldman Sachs expects Vietnam’s exports to continue growing.
Secondly, Vietnam’s structure of export products with a focus on hi-tech items would continue to be a major plus point for Vietnam. Since 2015, export turnover of products such as smart phones and electronic appliances have exceeded that of traditional items like textile or footwear.
In the January – August period, Vietnam’s export turnover of electronic products increased by 6.3% year-on-year amid the Covid-19 pandemic, accounting for 70% of total exports.
Thirdly, Vietnam’s long-standing trade partnership with China is also an advantage, as the latter would be among a handful of economies with a positive economic growth this year.
It is worth mentioning that China is currently Vietnam’s largest buyer.
In its baseline scenario, Goldman Sachs expects Vietnam’s exports to reach US$180 billion by the end of 2021, assuming the world would gradually contain the pandemic and the development of Covid-19 vaccine remains on track.